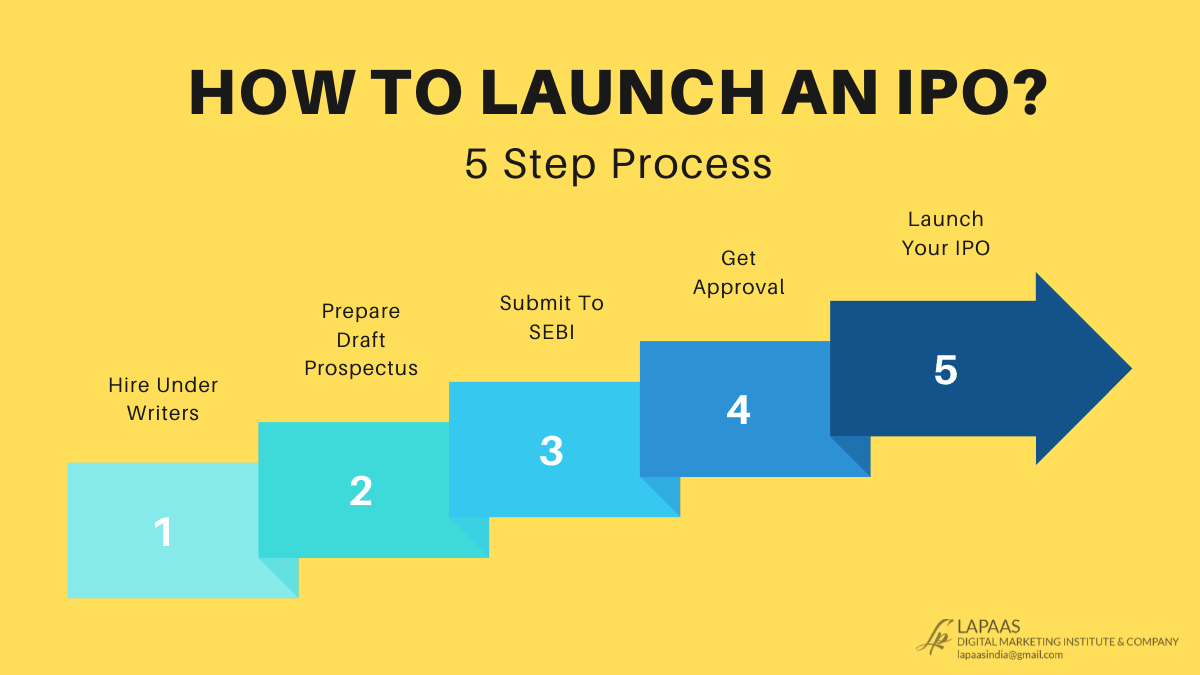
What is an IPO?
Initial public offering (IPO) can be defined as the process in which a private company or corporation can go public by selling a portion of its stake to investors. An IPO is typically initiated to infect the firm with new equity capital, to facilitate easy trading of existing assets, to raise capital for the future, or to monetize investments made by existing stakeholders.

Institutional investors, high net worth individuals (HNIs) and public can access details of the first sale of shares in the prospectus. The prospectus is a lengthy document that lists the details of the proposed offerings.
Once an IPO is made, the firm's shares are listed and can be freely traded in the open market. The stock exchange imposes a minimum free float on both the shares as a whole and in proportion to the total share capital.
IPO is an exciting time for a company. This means that it has become so successful that much capital is required to develop it. The only way for a company to get enough cash is for large-scale expansion. The funds allow the company to invest in new capital equipment and infrastructure. It can also pay off debt.
Stock shares are useful for mergers and acquisitions. If the company wants to acquire another business, it can offer shares as payment.
The IPO also allows the company to attract top talent as it can offer stock options. They will enable the company to pay its executives a much lower salary. In return, they have a promise that they can cash in later with the IPO.
There are two common types of IPO. They are:
Fixed Price Offer
Fixed price IPO can be referred to as the issue price that some companies set for the initial sale of their shares. Investors get to know the price of the shares that the company decides to make public.
The demand for shares in the market can be known after the issue closes. If investors participate in this IPO, they have to ensure that they pay the full price of the shares at the time of applying.
Book building offer
In the case of book production, the company initiating the IPO offers investors a 20% price band on the shares. Interested investors bid on the shares before the final price was decided. Here, investors are required to specify the number of shares they intend to buy and the amount they are willing to pay per share.
The lowest share price is referred to as the floor price and the highest stock price is referred to as the cap price. The final decision about the share price is determined by the investors' bids.

How to invest in an IPO?
There are some steps that an investor needs to follow to ensure that they are following the right path to wealth. The steps an investor needs to follow are:
Decision:
The primary step for an investor is to decide the IPO he wants to apply for. Although existing investors may have expertise, it can be a scare for newcomers. Investors can prepare an option by going through the prospectus of companies starting an IPO.
The prospectus helps investors to form an informed idea about the company's business plan and its purpose for raising stock in the market. Once a decision is made, the investor has to look forward to the next step.
Grant
When an investor has decided on an IPO, he would like to invest in it, then arranging the funds would be the next step. An investor can use his savings to buy part of the company.
If the investor does not have sufficient savings, he can get loans from certain banks and non-banking financial organizations (NBFCs) at a fixed rate of interest.
Demat-cum-Trading Account Opening
No investor can apply for an IPO without a demat account. The function of a demat account is to provide investors with a provision for electronically storing shares and other financial securities. A person can open a demat account by presenting his Aadhaar card, PAN card, address and identity proof.
Application Process
An investor can apply for an IPO through his bank account or trading account. Some financial organizations will provide you with a provision to bunch your demat, trading and bank accounts.
After an investor has created a demat-cum-trading account, he should be familiar with the application supported by the blocked account (ASBA) facility. It is mandatory for every IPO applicant. ASBA is an application that enables banks to arrest funds in an applicant's bank account.
The ASBA application form is made available to IPO applicants in both DMAT and physical forms. However, checks and demand drafts cannot be used to avail the facility. An investor has to specify his demat account number, PAN, bid details and bank account number in the application.
Bidding
An investor is required to bid when applying for shares in IPO