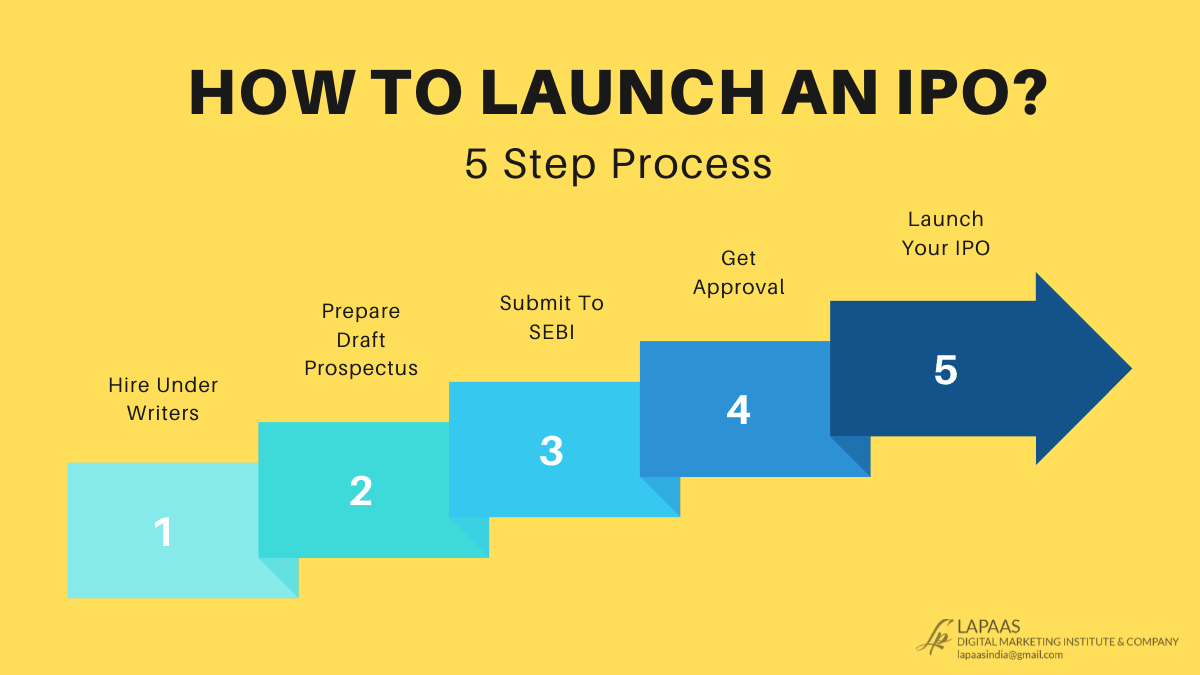
A patent is a form of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period in exchange for publishing a public disclosure of the invention. In most countries, patent rights fall under private law and the patent holder must sue a person for infringing the patent in order to enforce its rights. Patents are an essential form of competitive advantage in some industries; In others they are irrelevant.
Patents, requirements placed on patentees, and limits of exclusive rights vary widely between countries according to national laws and international agreements. Typically, however, a patent application must include one or more claims that define the invention. A patent may include multiple claims, each of which correctly defines a specific asset. These claims must meet the requirements of relevant patentability, such as novelty, usability, and non-legibility.

Under the World Trade Organization (WTO) TRIPS Agreement, patents must be available in WTO member states for any invention in all areas of technology, provided they are new, involve an inventive move, and are capable of industrial application. Nevertheless, there are differences between member countries of the World Trade Organization on what is a patentable subject from country to country. TRIPS also provides that the period of protection available should be a minimum of twenty years
Definition: What is a patent?
"A patent is a statutory right of an invention granted by the government for a limited period to a patent, in return for their invention to create, use, sell, import, or import others for a patented product or process. For full disclosure of. To produce that product for those purposes without his consent. "
In other words;
"A patent can be defined as the grant of exclusive rights to an inventor for a limited time on his invention (typically 20 years from the date of filing the patent application). Exclusive rights to others without their permission The right to sell, use, sell, import or present a patented invention is excluded. ”
This means, when you receive a patent for your innovative idea, the government grants a monopoly right to your invention to allow others to create, use, sell, import your patented invention without your permission. Or can stop visiting.
Patents have many potential advantages and disadvantages. When deciding whether you should apply for a patent, you should look at your invention and consider the risks of not getting a patent against the costs of doing so.
Benefits of patent
A patent gives you the right to prevent others from copying, manufacturing, selling or importing your invention without your permission. See protecting intellectual property.
You get protection for a pre-determined period of time, allowing you to keep competitors at bay.
Then you can use your invention.
Alternatively, you can license your patent to others to use it or you can sell it. This can provide an important source of revenue for your business. In fact, some businesses exist solely to collect royalties from a patent they have licensed - perhaps in combination with a registered design and trade mark. How to View Patent License

If you are considering gaining trade mark protection, see the benefits of trade mark registration.
Loss of patent
Your patent application means making certain technical information about your invention publicly available. It may be that keeping your invention a secret can keep competitors more effectively.
Applying for a patent can be a very time-consuming and lengthy process (usually three to four years) - by the time you receive the patent, the market may have changed or the technology may have overtaken your invention.
Cost - This will give you money whether you succeed or not - applications, discovery of existing patents and fees of a patent attorney can all contribute to a reasonable outlay. The ability to make a profit must surpass the time, effort, and money it takes to obtain and maintain a patent. Not all patents have financial value
You have to remember to pay your annual fee or your patent will be missed.
You have to be ready to defend your patent. Taking action against the violator can be very costly. On the other hand, a patent may act as a deterrent, making the defense unnecessary.
Patent Protection Benefits for Society
If you are patenting a product, I have listed three different patent protection benefits. These benefit patent protection, how patents are used to encourage innovation (ie, start a business) and provide a means by which to teach the public how your technology works. A patent is a means by which you can protect your invention with a patent rather than a trade secret.